
To see them with the ls command, add -a or -A at your ls. in Linux and Unix systems, the files starting with. To toggle show/hide hidden files or folders use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + H. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Hidden files and folder have names that start with a. If you use desktop Linux, you can still see hidden files easily. Your email address will not be published. You can also use the -A option of the ls command to show hidden files but without the. But if you want, you can also make the tool display files in reverse order.

We can list all the files in a different directory using ls C:\path\to\directory -Force. By default, the ls command displays the files alphabetically in the output. We used the command to display the hidden files. For example, the -Force parameters show all the files, including hidden files, of a specified directory. The ls command holds many different parameters to modify its behaviour. The output of the command includes file and directory names and information about each file, such as name, size, permissions, and last modified date.
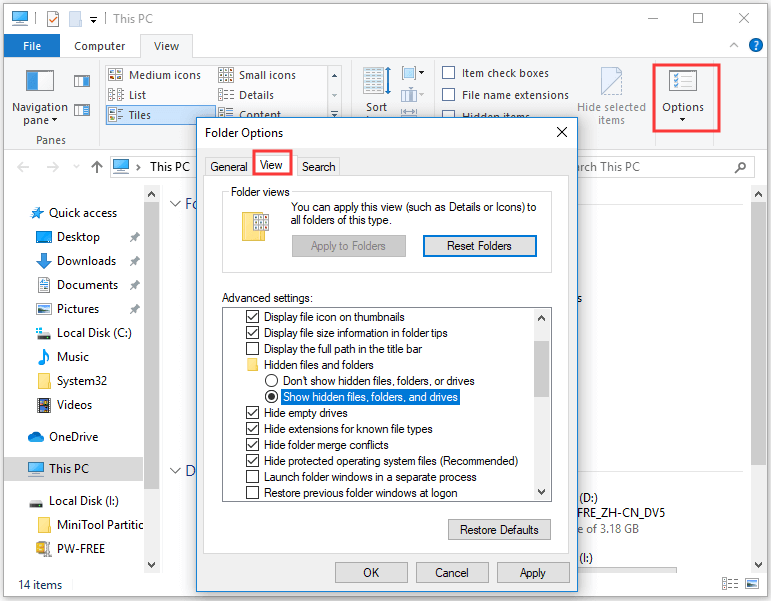
#Make ls show hidden files windows#
It is similar to the Windows dir command. In computing, the ls command lists the contents of the specified directory. It is an alias for the Get-ChildItem cmdlet, which we discussed while explaining the use of Get-Children. This is a common question for those new to PowerShell. You are not alone if you are wondering what the ls command is in PowerShell.
#Make ls show hidden files how to#
Knowing how to use this command is essential for effectively navigating and managing files on your system. Users of Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux and macOS, depending on the ls command as a fundamental tool. To show hidden files with other files, use the ls cmdlet with the -Force parameter. In addition, the script block used the -match operator to match the property’s value against the pattern hidden. For example, the -Property and -Match parameters specify the property to utilize and the pattern to match against the property value, respectively.įor example, we specified a script block with the -FilterScript parameter to filter the objects according to the value of the Attributes property. Several parameters in the Where-Object cmdlet define the standards for filtering the objects. As a result, the output of the Get-ChildItem cmdlet is piped to the Where-Object cmdlet. For example, we combined the Where-Object cmdlet with the Get-Children cmdlet. It is frequently combined with other cmdlets to filter the output depending on predetermined criteria. It accepts a collection of objects as input and returns a new collection containing only those objects that meet the given requirements.

In this section, we utilized PowerShell’s Where-Object cmdlet that filters the objects in a collection depending on a given criterion.

If no file or directory is specified, ls will display the contents of the current directory. The ls command is used in the following format: ls It can also be used to display detailed information about files and directories, such as permissions, ownership, and file size.
The ls command can be used to list files and directories in the current directory, or in a specified directory. It is used to display a listing of directory contents. You can modify your zsh and/or bash configuration files to do this. The ls command is one of the most commonly used commands in Linux. To ultimately make vanilla ls aware of the hidden files, you will need to alias ls to ls -G (and you get color too).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
